M.UNION Verified Suppliers in China, provides quality made in China products and certified China manufacturers. All China manufacturers in manufacturer-union.com are certificated by manufacturer union.
Recommended Enterprises
You Are Here: About Company » Products Categories » other products » Electric vehicle (EV) charging station
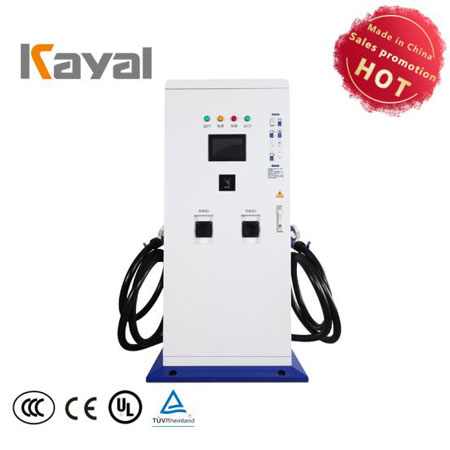
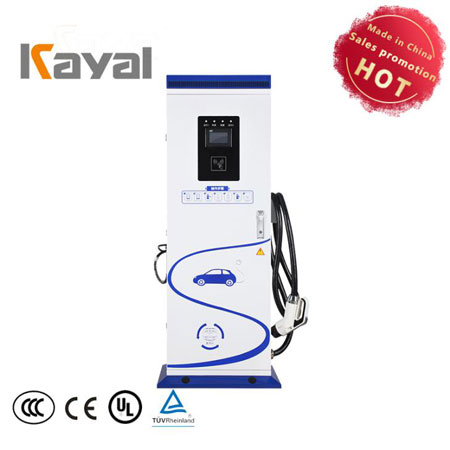
Electric vehicle (EV) charging station

Electric vehicle(EV) charging station
An electric vehicle charging station is a site for charging electric vehicles. With the popularity of electric vehicles, electric vehicle charging stations will become the focus of the automotive industry and energy industry development. Electric vehicle charging station can better solve the problem of fast charging, energy saving and emission reduction.
Chinese name: Electric vehicle charging station
Function: car charging
Service: Electric car
Features: Green
table of Contents
1 background
2 configuration
▪ Regular charging
▪ Fast charging
▪ Mechanical charging
▪ Portable charging
3 charging method
4 design
▪ Business model
▪ System structure
5 development
▪ Japan
▪ Europe
▪ China
6 interference source
background
The development of electric vehicle charging stations in China is inevitable, and the preemption is also the enterprise system.
The way to victory. Under the current circumstances, although the country has vigorously advocated, and enterprises are eager to move, it is not easy to do electric vehicles into ordinary people's homes in the short term. National policies can give (car compensation, roads, etc.), while electric vehicle charging station network can not be built in a short-term, the main reason is that the rapid charging of electric vehicles requires instantaneous and powerful power, the conventional power grid can not be met, and a dedicated charging network must be built. This involves the transformation of the entire national power grid. The transformation of the national power grid is not a trivial matter, and it is costly. From discussion, project establishment to network formation, it can be realized overnight.
The solution that can better solve the problem of fast charging is to replace the power station - to replace the long charging process by replacing the battery with the car. A car needs to be equipped with two batteries. When one battery is used up, it will automatically switch to another one. At this time, you can replace the used battery in the power station and install a fully charged battery. The replaced battery is uniformly charged and maintained by the power station, provided that the charging station has a considerable number of spare batteries. The advantage of this method is that the user can get on the road after changing the battery, which is faster than refueling. In this way, plus the auxiliary means such as parking lot charging piles, I believe that the popularity of electric vehicles is close at hand.
Configuration
Regular charging
1 Scale of a typical conventional charging station
According to the current data of conventional electric vehicle charging, a charging station is generally configured with 20 to 40 electric vehicles. This configuration is considered to fully utilize the evening valley electricity for charging, and the disadvantage is that the utilization rate of the charging device is low. When charging is also considered at the peak, 60-80 electric motors can be used to prepare a charging station. The disadvantage is that the charging cost increases and the peak load increases.
2 Typical configuration of the power station of the charging station (provided that the charging cabinet has harmonic processing functions)
a program:
Construction of the substation design 2 road 10KV cable incoming line (with 3 * 70mm cable), 2 sets of 500KVA transformer, 24 way 380V outlet. The second way is the special charging line for fast charging (with 4*120mm cable, 50M long, 4 loop), the second way is mechanical charging or spare outlet, and the rest is regular charging outlet (with 4*70mm cable, 50M long, 20 loop)
Scheme b:
Design 2 road 10KV cable (with 3*70mm cable), set 2 sets of 500KVA user box change, each box is equipped with 4 channels 380V outlet (with 4*240mm cable, 20M long, 8 loop), set one for each outlet The 4-circuit cable branch box supplies power to the charging cabinet (with 4*70mm cable, 50M long, 24 loops).
fast charging
1 Scale of a typical fast charging station
According to the current data of rapid charging of electric vehicles, a charging station is generally configured to charge eight electric vehicles at the same time.
2 Typical configuration of charging station power supply
a scheme, construction of substation design 2 road 10KV cable incoming line (with 3 * 70mm cable), 2 sets of 500KVA transformer, 10 way 380V outlet (with 4 * 120mm cable, 50M long, 10 loop).
b scheme, design 2 road 10KV cable (with 3*70mm cable), set 2 sets of 500KVA user box change, each box is equipped with 4 channels 380V outlet for charging station (with 4*120mm cable, 50M long, 8 loop ).
Mechanical charging
1 mechanical charging station scale
Small mechanical charging stations can be combined with conventional charging station construction, and larger capacity transformers can be selected as needed. Large mechanical charging stations are generally equipped with a large mechanical charging station with 80~100 rechargeable batteries. It is mainly used in the taxi industry or battery rental industry. It can complete the charging of 400 batteries in one day without interruption.
2 Typical configuration of charging station power supply (large mechanical charging station)
2 road 10KV cable entry (with 3*240mm cable), 2 1600KVA transformers, 10 380V outlets (with 4*240mm cable, 50M long, 10 loops).
Portable charging
1 Villa
With a three-phase four-wire meter, an independent parking garage, you can use the existing residential power supply facilities, from the residential distribution box to a dedicated 10mm2 or 16mm2 line to the dedicated socket of the garage to provide portable charging power.
2 General residence
It has a fixed centralized parking garage, and generally requires an underground parking garage (for charging safety considerations). It can be reconstructed by using the original power supply facilities of the community. It must be considered according to the existing load capacity of the residential area, including the load of the valley electricity. The specific plan should be determined according to the power supply facilities and schemes of the community and the building environment of the community.
Charging method
After the electric vehicle battery is discharged, the battery is returned to the working capacity by direct current in the opposite direction to the discharge current. This process is called battery charging. When the battery is charged, the positive pole of the battery is connected with the positive pole of the power supply, the negative pole of the battery is connected with the negative pole of the power supply, and the voltage of the charging power supply must be higher than the total electromotive force of the battery. There are two types of charging methods: constant current charging and constant voltage charging.
Research on charging method of electric vehicle charging technology:
The conventional charging system was designed based on internationally accepted rules of thumb before 1940. The most famous of these is the "Ampere Hours Rule": the charging current amperage should not exceed the number of hours the battery is to be charged. In fact, the speed of conventional charging is limited by the temperature rise of the battery during charging and the generation of gas. This phenomenon is important for the shortest time necessary to charge the battery.
Constant current charging method
The constant current charging method is a charging method in which the output voltage of the charging device is adjusted or the resistance in series with the battery is changed to maintain the charging current intensity. The control method is simple, but since the acceptable current capability of the battery is gradually decreased as the charging process progresses, the charging current is mostly used to electrolyze water and generate gas to make the gas out too late. Therefore, the stage charging method is often used.
Stage charging method
This method includes a two-stage charging method and a three-stage charging method.
The two-stage method employs a fast charging method in which a constant current and a constant voltage are combined. First, charging with a constant current to a predetermined voltage value, and then changing to a constant voltage to complete the remaining charging. Generally, the conversion voltage between the two phases is the constant voltage of the second phase.
The two-stage charging method uses constant current charging at the beginning and end of charging, and is charged with a constant voltage in the middle. When the current decays to a predetermined value, the second phase is switched to the third phase. This method can minimize the amount of gas output, but it is limited as a fast charging method.
Constant voltage charging method
The voltage of the charging power source maintains a constant value throughout the charging time, and the current gradually decreases as the voltage at the battery terminal gradually increases. Compared with the constant current charging method, the charging process is closer to the optimal charging curve. Fast charging with a constant voltage, because the battery electromotive force is low at the initial stage of charging, the charging current is large, and the current will gradually decrease as the charging progresses, so only a simple control system is needed.
This charging method seldom electrolyzes water and avoids overcharging of the battery. However, in the initial stage of charging, the current is too large, which has a great influence on the battery life, and it is easy to bend the battery plate and cause the battery to be scrapped. In view of this drawback, constant voltage charging is rarely used, and is only used when the charging power supply voltage is low and the current is large. For example, during the operation of a car, the battery is charged by a constant voltage charging method.
Fast charging method
1 pulse charging method, this charging method not only follows the inherent charging acceptance rate of the battery, but also can improve the charging acceptance rate of the electric vehicle battery, thereby breaking the limitation of the battery index charging acceptance curve, which is also a new development of the battery charging theory.
22REFLEXTM fast charging method, which is a patented technology in the United States, it mainly faces the charging of nickel-cadmium batteries. Because it adopts a new charging method, it solves the memory effect of the nickel-cadmium battery, thus greatly reducing the time for rapid charging of the battery. The charging method of the lead-acid battery and the detection method of the charging state are very different from those of the nickel-cadmium battery, but one working cycle of the REFLEXTM charging method can be mutually used, including a forward charging pulse, a reverse instantaneous discharging pulse, and stopping. Charge to maintain 3 stages.
3 variable current intermittent charging method, this charging method is based on constant current charging and pulse charging, as shown in Figure 7. It is characterized by changing the constant current charging section to a voltage limiting variable current intermittent charging section. In the early stage of charging, the method of variable current intermittent charging is adopted to ensure that the charging current is increased and most of the charging amount is obtained. In the later stage of charging, a constant voltage charging section is used to obtain an overcharge amount, and the battery is restored to a fully charged state. By intermittently stopping the charging, the oxygen and hydrogen generated by the chemical reaction of the battery are recombined and absorbed, and the concentration polarization and the ohmic polarization are naturally eliminated, thereby reducing the internal pressure of the battery and enabling the next round. The constant current charging can be performed more smoothly, so that the battery can absorb more power.
4 variable voltage intermittent charging method, based on the variable current intermittent charging method, a variable voltage intermittent charging method has been proposed, as shown in FIG. The difference from the variable current intermittent charging method is that the first stage is not intermittent constant current but intermittent constant pressure. In each constant voltage charging phase, due to constant voltage charging, the charging current naturally decreases exponentially, which is consistent with the battery current acceptability rate gradually decreasing with the charging.
5 variable voltage variable current wave type intermittent positive and negative zero pulse fast charging method, combined with pulse charging method, ReflexTM fast charging method, variable current intermittent charging method and variable voltage intermittent charging method, variable voltage variable current wave positive and negative zero pulse The intermittent fast charging method has been developed and applied. There are two types of control for the charging circuit of the pulse charging method:
1) The amplitude of the pulse current is variable, and the frequency of the PWM (drive charge and discharge switch) signal is fixed;
2) The amplitude of the pulse current is fixed, and the frequency of the PWM signal is adjustable.
The amplitude of the pulse current and the frequency of the PWM signal are fixed, and the PWM duty ratio is adjustable. On this basis, the intermittent charging and charging phase is added, which can charge more power in a shorter time and improve the charging acceptance of the battery.
design
Business model
The charging business model refers to a model in which an electric vehicle user selects a charging station and a charging station to directly charge the battery of the automobile when the vehicle power is exhausted. This is the first business model considered by electric vehicle charging stations. In this business model, electric vehicle users complete the transaction by charging the car directly at the charging station/charging pile, instantly consuming the power product and paying the fee through the on-site payment model. . To this end, the construction of a corresponding electric vehicle charging and billing system and the introduction of a centralized information management platform are important components for the construction of electric vehicle charging and discharging stations.
system structure
The charging station can be divided into four sub-modules according to functions: power distribution system, charging system, battery dispatching system, charging station monitoring system. Charging stations charge cars in three ways: normal charging, fast charging, and battery replacement. Ordinary charging is mostly AC charging, and 220V or 380V can be used. Fast charging is mostly DC charging. The main equipment of the charging station includes a charger, a charging pile, an active filtering device, and a power monitoring system.
1. Establish a charging and billing system management platform to centrally manage the basic data involved in the system, such as electric vehicle information, power purchase user information, and asset information.
2. Construction of a charging and billing system operation platform for operation and management of charging and discharging of electric vehicles and recharging of power users.
3. Build a charging and billing system query platform for comprehensive query of relevant data generated by the management platform and operation platform.
development of
The construction of charging stations and small charging piles and other facilities can also be converted into charging stations. This type of charging station is similar to a gas station, but the investment cost is only 10% of that of a regular gas station, and the safety requirements are lower than that of a gas station.
Japan
In Japan, a close partnership with various automakers is the largest power company in Japan, Dongdian. Not long ago, it successfully developed a large fast charger, which greatly shortened the charging time and further increased the possibility of popular use of electric vehicles in Japan. Dongdian pointed out that every 10 minutes of full charge, the distance traveled is 60 kilometers. In order to make it easier for drivers to charge when they go to the streets, they must be promoted through a large-scale infrastructure construction project. At the same time, Dongdian also announced that it will introduce 3,000 electric vehicles for business and service purposes based on considerations such as “environmental protection” and “economics”.
The fee for each charger is 4 million yen. The company is preparing to build chargers in public places such as supermarket parking lots, convenience stores and post offices in Japan. It allows people to get off the bus and make the car replenish power when doing business. The Japanese auto industry believes that electric vehicles are suitable for urban driving. It is expected that as long as the charging infrastructure is fully equipped, it will soon be accepted by the general consumers.
Europe
France sponsors the long-term innovation of electric vehicles and their parts and components. The French power company is the leading power company to prepare a budget of more than 110 million francs per year (accounting for 0.05% of the company's operating income), investing in the research and development of batteries and chargers, and setting up hundreds in Paris. Chargers, all important parking lots have chargers, and special plugs for charging electric vehicles.
Germany also plans to waive the electric vehicle tax and weight tax within 5 years; the company can enjoy a five-year tax-free charging station for most of the charging stations (68%), which is completely free, and a small part of the charging fee or parking fee.
China
In April 2009, Nissan Motor and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China established a cooperative relationship. Nissan Motor will provide the Ministry of Industry and Information with information on the development of electric vehicles, and develop a comprehensive plan that includes the establishment and maintenance of battery charging networks and the promotion of large-scale use of electric vehicles. Wuhan will become the first pilot of Nissan's implementation of its zero-emission vehicle program in China. In the future, Wuhan must follow Nissan's standards, which will establish Nissan's dominant position in the competition of electric vehicles.
According to news from Shenzhen on July 14, 2009, the city may purchase BYD's 30 dual-mode electric vehicles as taxis in the future. According to BYD's introduction, the F3 dual-mode electric vehicle consumes 16 degrees of electricity per 100 kilometers, about 9 yuan. A person in charge of BYD said that BYD has built a number of charging piles in Shenzhen to solve the problem of electric vehicle charging, but the scope is limited to the vicinity of the main city of Shenzhen.
The local policies of Anhui Province also pointed out that in the future, new buses and taxis in the city will purchase hybrid electric vehicles and pure electric vehicles produced in Anhui Province, and implement registration management for new energy vehicles that meet the safety technical requirements of motor vehicles, and reduce new energy vehicles. Various taxes and fees support the construction land and supporting funds for electric vehicle charging stations.
In July 2015, Qinghai's first optical storage integrated electric vehicle charging station was completed and put into operation. It is reported that the optical storage integrated electric vehicle charging station is the 2015 Science and Technology Support Project of the Science and Technology Department of Qinghai Province, with a total investment of about 2 million yuan, which is a permanent charging station. The charging station integrates many advanced technologies such as photovoltaic power generation, intelligent charging piles and energy storage batteries, which breaks through the bottleneck that photovoltaic power plants cannot charge electric vehicles at night.
The optical storage integrated electric vehicle charging station has a photovoltaic installed capacity of 35 kilowatts, a daily generating capacity of about 200 degrees, and an energy storage capacity of 150 kilowatt hours. There are 12 charging piles, which can provide DC fast charging and communication for all major domestic and international brands of electric vehicles. Slow charging service. At present, State Grid Qinghai Electric Power Company has built 9 charging stations in Xining, Haibei and Hainan, erected 7.2 kilometers of 10 kV lines, installed one high-voltage ring network cabinet, 15 transformers, and 32 sets of 7-kilowatt slow charging piles. 36 sets of 40 kilowatt fast charging piles and 3 sets of 100 kilowatt fast charging piles. [1]
First, the distance between pure electric vehicles and large-scale promotion There are still many technical problems to be solved in pure electric vehicles. First of all, it is the cruising range of pure electric vehicles. Experts believe that the maximum speed of the Zotye car and the power consumption of 100 kilometers are all achievable, but the cruising range of 300 kilometers may be only the theoretical calculation or the index reached when driving at a constant speed of 30-40 km/h. In working conditions, it is difficult for a pure electric vehicle to reach a cruising range of 300 kilometers. The short-distance cruising range brings a lot of inconvenience to many car owners, which greatly limits the promotion of pure electric vehicles. Second, the charging of pure electric vehicles is also a problem. At present, the charging time of pure electric vehicles generally takes 7-8 hours. Although some batteries can be charged in a short time, this greatly shortens the battery life. And such a long charging time has also become an obstacle to the acceptance of electric vehicles. The domestic supporting infrastructure is still lacking. If you want to promote pure electric vehicles, you need a large number of charging stations, like the current gas station can make the car easy to charge. Finally, the current battery life and cost are also an obstacle to industrialization.
Second, the current bus is a direction for the development of pure electric vehicles
Due to the fixed bus line, unified management and low speed, it has become a good platform for the promotion of pure electric vehicles. On the one hand, the bus line is fixed, so that the mileage of the bus can be controlled within the battery's cruising range. The bus can be managed in a unified manner, and the bus can be charged in the evening. This can solve the problem of pure electric vehicle cruising range and inconvenient charging. On the other hand, because the speed of the bus is not high, the performance of the battery can meet the requirements of its power. At the same time, taxis that are fixed short-distance can also be the target of pure electric vehicles.
Third, the prospects for the development of electric vehicles
Pure electric vehicles have many advantages. Because pure electric is more environmentally friendly than traditional cars, and the control of pure electric vehicles is actually simpler than hybrid cars. On the one hand, hybrid vehicles need to control the engine. On the other hand, they need to control the battery and the motor, and the motor and the engine work well. The technical difficulty is high. In comparison, the motor torque and power required by the pure electric vehicle are high. Control is simpler and the motor responds faster. At present, the main problem to be solved is the problem of the battery, which is to improve the life of the battery, increase the cruising range and reduce the cost. Battery management and scrap recycling are also considered. The professor of Tongji University suggested that in the future, the owner can supplement the electric energy by changing the battery at the charging station, so that the owner does not need to wait for the charging time, which is convenient and quick, and the charging station also realizes the unified charging and management of the battery, and improves the battery life. And the recycling of convenient old batteries is a good solution. With the further improvement of battery performance and the improvement of supporting facilities and management solutions, pure electric vehicles still have broad development prospects.
On June 27, 2014, the “Beijing Electric Vehicle Promotion and Application Action Plan (2014-2017)” was released in Beijing on the 27th. According to the plan, Beijing will speed up the construction of fast charging piles in public places. By 2017, there will be 10,000 fast charging piles in the city to be exposed to public parking lots and other places.
Beijing plans to build 10,000 electric vehicle fast charging piles, which will be mainly concentrated in public parking lots, transportation hub parking lots (including P+R), large-scale commercial super parking lots, highway service areas, and electric vehicle professional marketing (4S) stores. Conditions such as gas stations and other places, to facilitate the travel of electric vehicles. [2]
Interference source
The electromagnetic environment of an electric vehicle refers to the electromagnetic interference of various electric electromagnetic interferences from the interior and exterior of the vehicle and the electromagnetic interference radiated by the electric vehicle and electronic equipment to the outside during the operation of the electric vehicle. The electrical and electronic equipment on the vehicle should be able to maintain normal operation under such circumstances, without performance degradation or even damage. Since electric vehicles can be used in various places, the electromagnetic environment is also very different. Electromagnetic interference of electric vehicles can be roughly divided into three categories, namely, vehicle interference sources, natural interference sources, and human interference sources.
1. Vehicle interference source
The vehicle interference source mainly refers to the electromagnetic interference generated by the electronic and electrical system on the vehicle.
Electric vehicle charging station
Electric vehicle charging station
Various transient voltages appearing in electric vehicle circuits, or sparks and arcs generated between contacts at the moment of circuit breaking, may affect the normal operation of sensitive equipment on the vehicle. Vehicle interference sources mainly include electronic systems such as drive systems, power batteries, power converters, relays, point assist systems, switches, communication equipment, and microprocessors. Both the rapid transients of voltage and current generate radiation and noise. Electronic devices closer to these devices may cause malfunctions, especially the rapid rectification of motor drive modules, motor starting, and high-voltage radiation may cause higher field strength conduction. Conform to harassment.
The electromagnetic propagation mode of the vehicle interference source is very complicated, and it has two forms of conducted interference and radiation interference. Conductive coupling requires a complete circuit connection from the receiver, usually with 3 coupling paths: common source, common loop and near-field coupling between the conductors, both of which are conductive coupling.
In general, in the radiated interference of electric vehicle systems, common mode high frequency interference dominates, while other frequency bands have less interference. The noise caused by the action of the switching elements of the drive system propagates through the common mode and differential mode loops. The DC bus or cable connected to the battery and the converter is connected to the AC motor of the AC motor and the converter. A large transient current flows through the current. Radiation can be emitted outwards through long wires or by adjacent wires through crosstalk. Due to the space and structure of electric vehicles, coupling and crosstalk inevitably occur in electric vehicle high-voltage wires and mortgage control lines.
2, natural interference
The source of natural interference is electromagnetic interference caused by natural phenomena. The electromagnetic noise generated by typical natural electromagnetic phenomena includes atmospheric noise, solar noise, cosmic noise, and electrostatic discharge. In most cases, this electromagnetic noise is very complicated and the interference effects on electric vehicles are negligible. However, lightning and electrostatic discharge can produce large transient field strengths. Lightning is a very complex process with currents in excess of 10kA and rise times of less than 1 microsecond. There are few direct clicks on electric vehicles, but the field strength caused by lightning is very large. At 200m, 100Kv/m is 4V/m at 175 km. The friction between the passenger and the seat and the friction of the electric vehicle body with the air during the driving process are all accumulating static electricity. When the high-voltage static electricity is discharged, it will affect the operation of the electronic device and even cause permanent damage.
3. Human interference sources
The human interference source refers to the electromagnetic interference generated by the external artificial device of the electric vehicle, mainly the radiation interference of other vehicles, the electromagnetic wave interference emitted by the radar outside the vehicle, the radio station transmitter, the mobile communication device, and the corona of the high voltage transmission line. Discharge, etc.
The electric vehicle charging station opened in the space bridge, Majialou, Xiaoying, Sihui and other places has a technical basis. Yesterday, the Municipal Quality Supervision Bureau issued the standardization technical documents of the "Electric Vehicle Power Supply and Protection Technical Specification Charging Station", which stipulated the classification, function, composition, technical requirements and site selection requirements of the city's charging stations.
The standard divides the charging station into four levels according to the storage capacity of the power battery and the charging service capability. The storage capacity of the storage battery of the first-level charging station is not less than 6800 kWh, or the single-channel power distribution capacity is not less than 5000 kVA, and the battery can be provided for more than 200 large and medium-sized commercial vehicles or more than 500 passenger cars per day. Replace or charge the service. The storage capacity of the battery of the four-stage charging station is less than 1700 kWh, or the single-channel power distribution capacity is less than 1000 kVA. The battery can be replaced by a large and medium-sized commercial vehicle of less than 40 times per day or a passenger car of less than 100 times. Charging service.
According to the principle of land saving and the use characteristics of electric vehicles, the standard proposes that the charging station should be built in conjunction with the existing public service facilities. After the construction, the safety and function of the original facilities should not be affected. According to the traffic impact assessment, the charging station in the city should be close to the urban road, but it should not be set at the intersection of the urban trunk road and the busy traffic section. Among them, the electric vehicle charging station for public transportation should be set in the bus station, and other special electric vehicle charging stations are set in the corresponding stop station. The charging station should not be located in places with severe vibration, high temperature, low terrain and possible water accumulation. When the charging station is in close proximity to dusty or corrosive gases, the downwind direction should be set at the minimum frequency.
An anti-collision column (column) shall be provided near the charging station charger, and its height shall not be less than 0.8 m. The charging connector of the charger should have obvious text and warning signs. The charging station should post a safety warning sign, a fire safety sign and an image acquisition area mark in a conspicuous position, and set an automatic fire alarm device. A flammable gas alarm system should be installed in the charging area, battery storage area and the like. The charging station built with the refueling station, the distance between the battery charging equipment, the battery replacement facility and the boundary line of the hazardous area of the dangerous equipment and the outer edge of the diesel equipment shall not be less than 3 meters.
In addition, the standard also specifies the lanes and parking spaces of charging stations. The entrance and exit of the charging station should be set separately, with at least 2 lanes from the entrance to the exit. The width of the lane in the charging station is not less than 4 meters, and the turning radius of the road inside the station should not be less than 9 meters. The asphalt area should not be used in the charging area, battery storage area and replacement area.
Products Categories
New Products